The Kinetic Intelligence Machine (KIM) Lab at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign has introduced Ringbot, a groundbreaking monocycle robot prototype. Unlike traditional monocycles, Ringbot doesn’t require a human driver or conventional driving components. Instead, it features compactly mounted legs within its wheel body.
In the realm of science fiction, futuristic technologies often inspire real-world innovations. Humanoid robots, once confined to the pages of novels and the screens of movies, are now on the brink of becoming household staples. Similarly, while bicycles have long been a standard mode of transportation, electric unicycles have emerged as a faster alternative with a smaller footprint, gaining popularity as a choice for urban commuters.
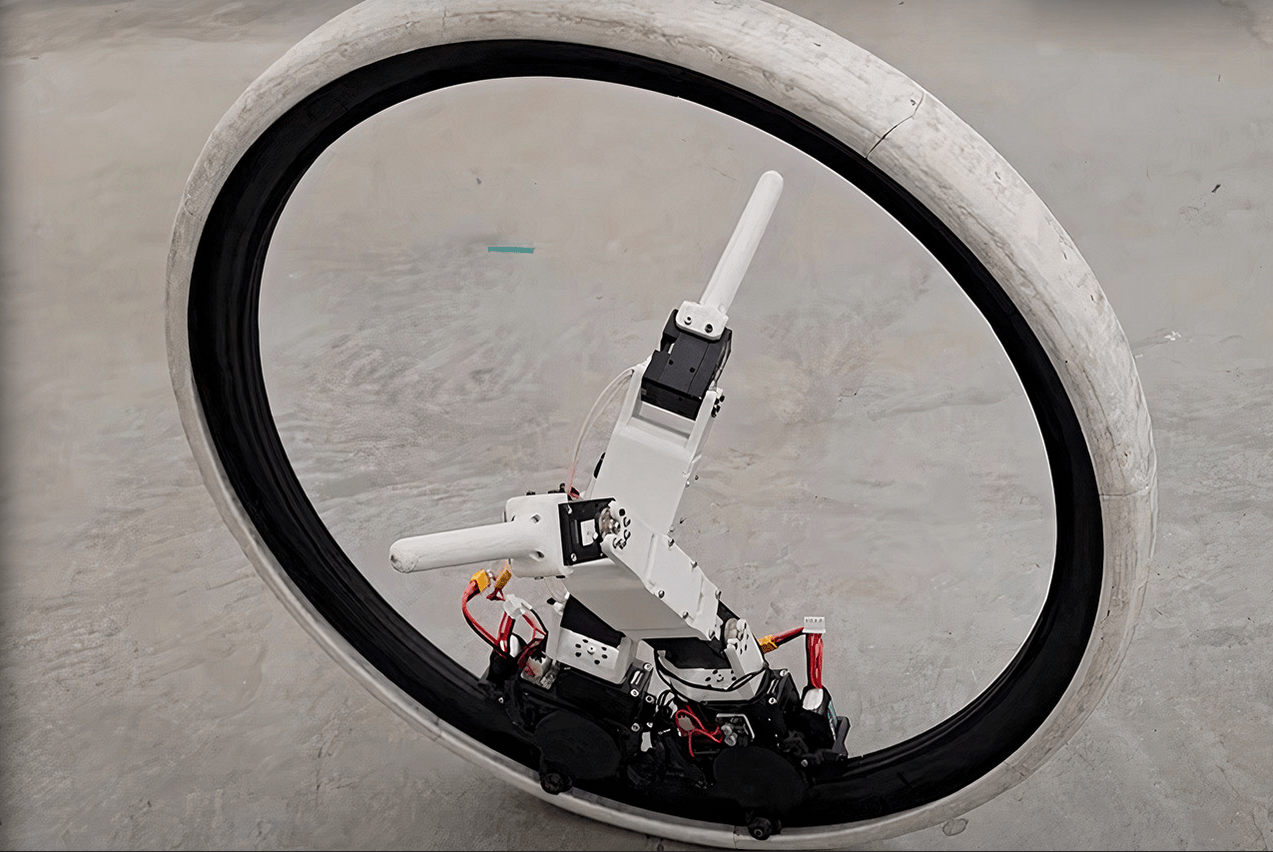
The concept of monowheels, reminiscent of science fiction movies, is gaining traction due to their potential to address urban transportation challenges. Monowheels could offer a compact, city-friendly alternative to traditional cars, particularly for solo travelers. Engineers and students have showcased their attempts at building monowheels, but the Illinois researchers have taken a significant leap forward by developing Ringbot, which operates autonomously without a human driver.
Ringbot features two independent driving modules housed within its wheel body. These modules can control velocity and orientation, even making full rotations within the wheel when necessary. Despite being a prototype, Ringbot can travel at speeds exceeding three miles per hour and navigate independently without assistance for balancing or turning, thanks to its integrated legs.
The bot’s legs play a crucial role in maintaining stability. When the wheel loses balance, the legs provide support, helping Ringbot stand up. Once sensors confirm stability, the legs retract, allowing the driving modules to resume operation. Additionally, Ringbot can deploy its legs to turn in the desired direction, and its single-wheel design enables it to traverse small obstacles effortlessly.
Ringbot represents a significant step towards autonomous urban transportation. Its ability to self-balance and navigate obstacles showcases its potential for future applications in crowded city environments. While still in the prototype stage, Ringbot offers a glimpse into the possibilities of driverless mobility solutions. As researchers continue to refine its design and functionality, Ringbot may pave the way for innovative transportation alternatives in cities of the future.


