Introduction
An inductor is essentially a passive two terminal component and is capable of resisting changes in electric current that passes through it and eventually develops a magnetic field (stores energy) that can be used later. The inductor was invented back in 1807. The inductor has units of henry (ratio of voltage to the rate of change of current).
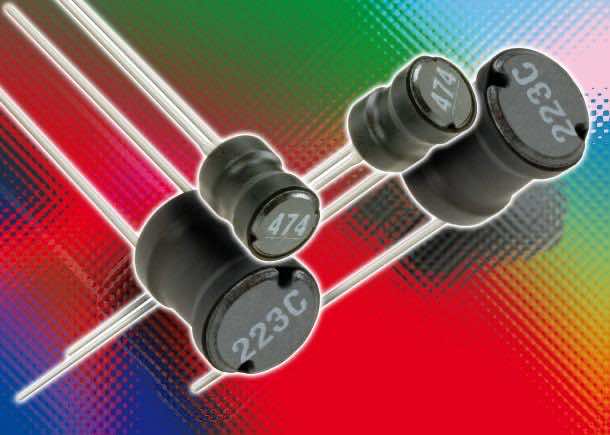

How Does An Inductor Work?
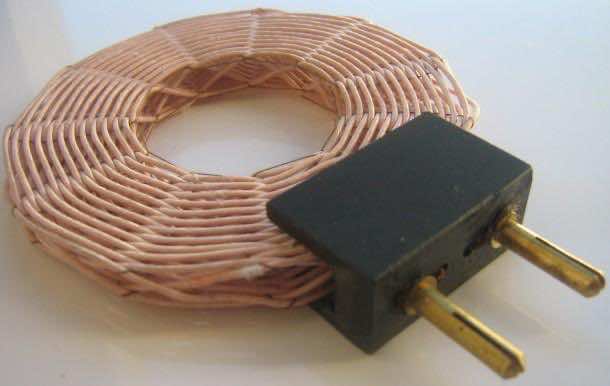
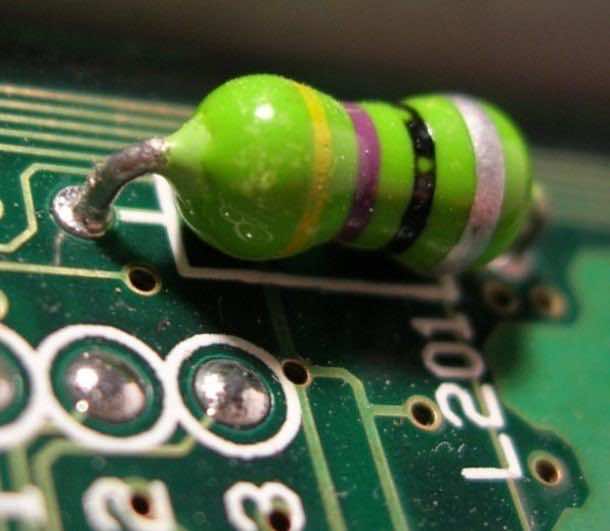 An inductor consists of loop(s) of a wire or coil. The inductance is directly proportional to the number of turns and when current passes through the loops, a magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field upon removal of current source is capable of generating current.
An inductor consists of loop(s) of a wire or coil. The inductance is directly proportional to the number of turns and when current passes through the loops, a magnetic field is generated. This magnetic field upon removal of current source is capable of generating current.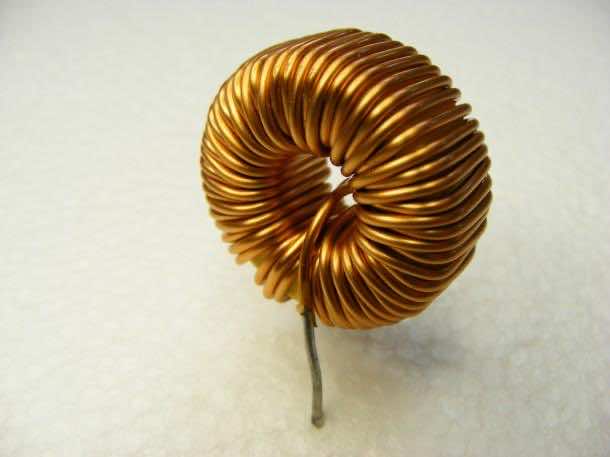 
Types Of Inductors
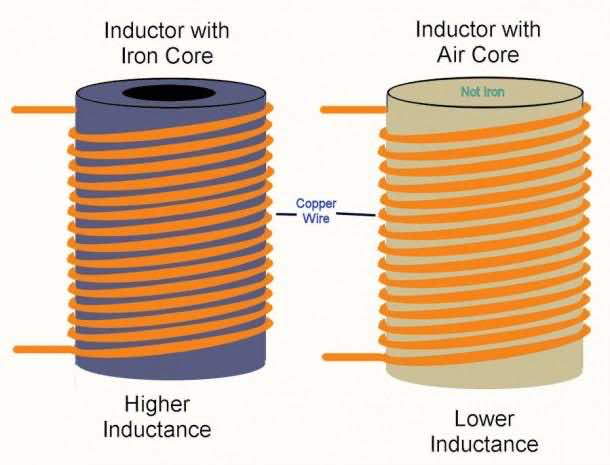
1. Air core inductor
o Radio frequency inductor
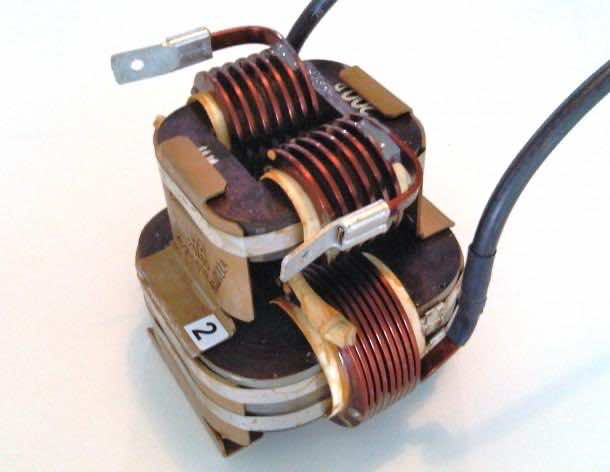
2. Ferromagnetic core inductor
o Laminated core inductor
o Ferrite-core inductor
o Toroidal core inductor
o Choke
Applications Of Inductors
· Filters
· Sensors
· Transformers
· Motors
Precautionary Measures
- Excessive shock should not be transferred to inductors especially while they are being mounted.
- Inductors should not be kept with magnetic items or magnets for that matter.
- Some inductors have polarity mentioned and this should be kept in mind when installing them.
- Keep inductors away from direct heat sources such as heaters and stove.








Very Informative post, I just bookmarked it for future reference. Thanks