The most widely used type of engine is combustion engine and although even under the name of combustion engines, you’d find a lot of variations, one thing is more or less always constant; they all adhere to the conventional combustion system in one way or another. The constant among all the variations is the fact that the output is usually some form of rotation; turbine blades, pistons and crankshafts. Toyota is working to change that by introducing a new type that it has named as Free Piston Engine Linear Generator (FPEG). What is so special about FPEG? It has no crankshaft and generates three phase electricity.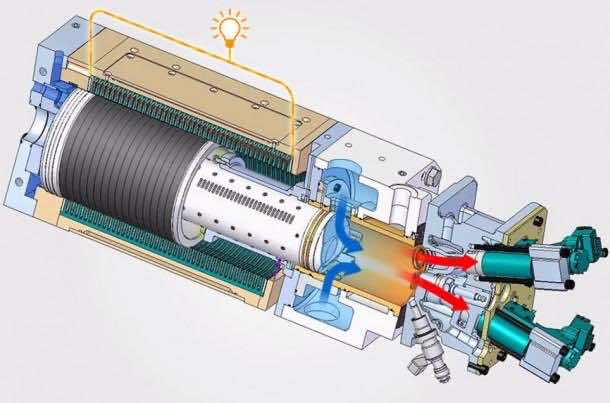
FPEG works in a peculiar way; during the power stroke of the cycle, the pistons are driven to push permanent magnets through a coil that is located around the cylinder chamber and that results in the production of electricity. So what is Toyota doing? It is combining two known processes; combustion engines and electromagnetic induction in this new type of engine. The reason why this setup is being given the limelight is because of the fact that as per Toyota, the thermal efficiency of FPEG is 42% and that is quite an improvement when you compare it to the thermal efficiency of the conventional combustion engine; 25-30%.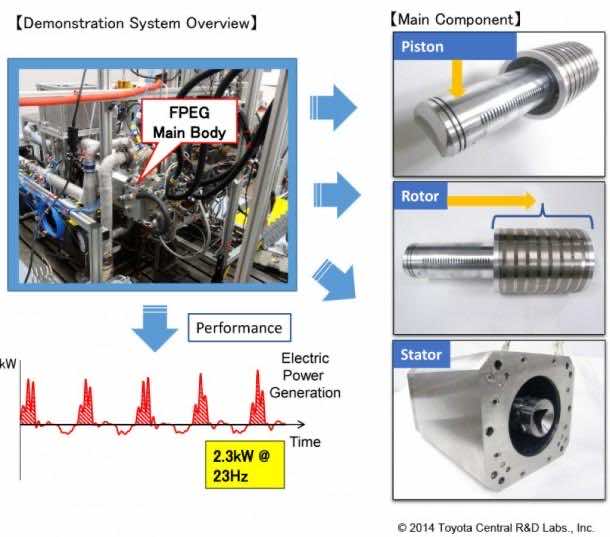
The engine is powered by either a diesel cycle or on standard gasoline without sparking. The two stroke cycle is depicted in the video and the fact that it is a two stroke engine, the chances of this being used in an automobile are slim because two stroke engines are discouraged because of higher emissions and noise. Despite that, Toyota says that a twin unit with a 20kW output shall be able to power a sedan (light one) to reach a speed of 120 Km/hr.
As to the question of returning the piston to the original position; gas springs have been incorporated at the end of chamber that creates the force required to compress the gas once again. There are no complex balances required since there is no moving crank shaft. The vibration issue has been tackled by using a twin unit design where each piston cancels out the other piston’s vibration.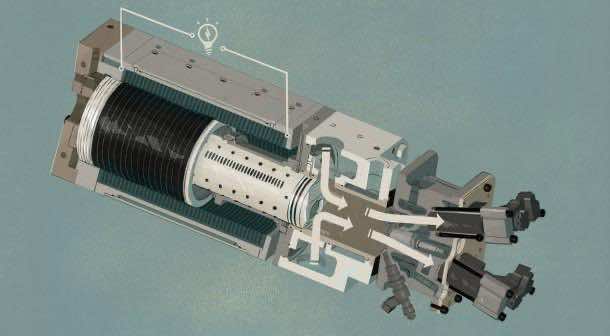
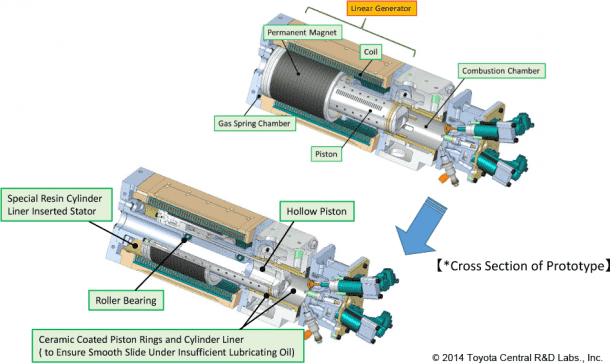
Toyota has already created a prototype that is about 2 ft in length and 8 inches in diameter and is capable of producing about 15 hp. The design is scalable, theoretically, and this can be transformed into something that is capable of generating higher power but there’s still some time before we get to witness where Toyota goes with this design.



Surely a gas spring only cushions/absorbs.It is not a return spring.Im no expert but a good cg would have helped.
this would save the energy required for the spring, greater than the energy required for compression, and double the energy with little increase in volume and weight. Combustion chambers at both ends of the piston, would be the logical next step.
this is a great innovation. I wonder if it is possible to power stroke the return of piston instead of a spring.