Despite the possibility of a six-month moratorium on AI development, GPT-4 has the potential for significant advancement with the use of a self-reflection technique called “Reflexion.”
This technique enables GPT-4 to evaluate its own performance by critiquing its answers and rewriting solutions based on the results. Researchers have used this technique to improve GPT-4’s performance in various tests.
“It’s not everyday that humans develop novel techniques to achieve state-of-the-art standards using decision-making processes once thought to be unique to human intelligence,” wrote researchers Noah Shinn and Ashwin Gopinath. “But, that’s exactly what we did.”
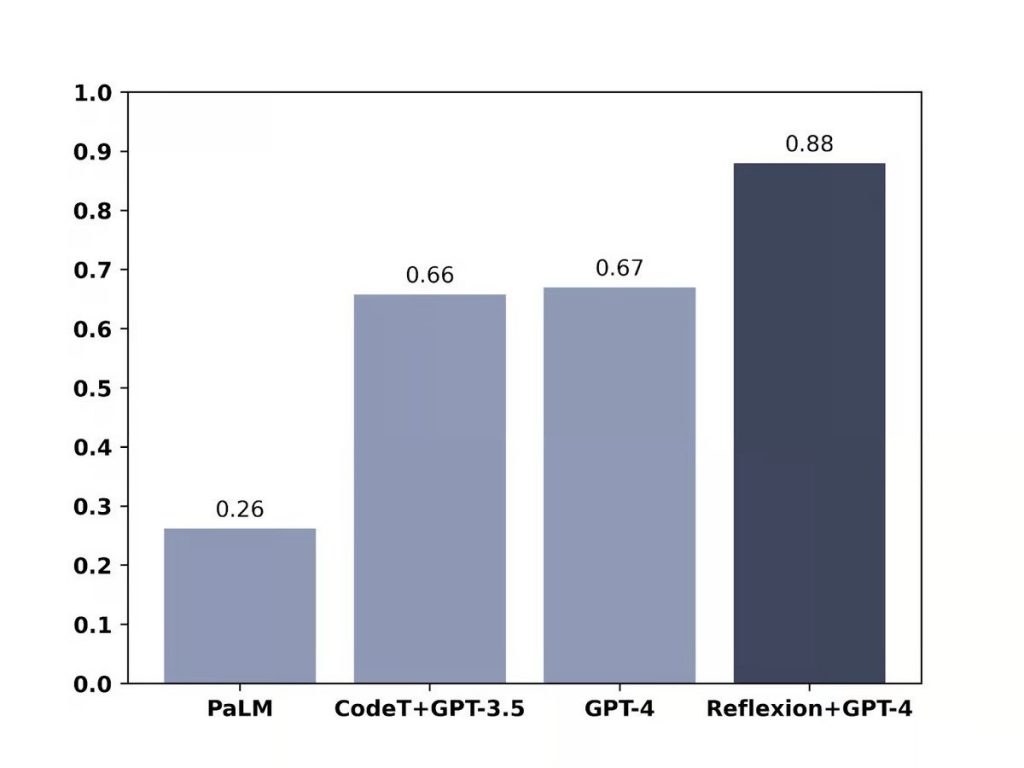
In the HumanEval test, which features 164 Python programming problems that GPT-4 has never seen before, its score increased from 67% to 88% with the Reflexion technique. Similarly, in the Alfworld test, which tests GPT-4’s ability to make decisions and solve multi-step tasks in interactive environments, its score improved from 73% to 97%, only failing on 4 out of 134 tasks.
In the HotPotQA test, which involves parsing content and reasoning over several supporting documents, GPT-4’s accuracy was initially 34%. However, with the use of the Reflexion technique, its accuracy improved to 54%, outperforming its previous score.
Increasingly, AI problems are being solved using AI itself. This approach is reminiscent of the generative adversarial network (GAN) method, in which two AIs collaborate to improve each other’s abilities.
For example, one AI generates images that are difficult to distinguish from real ones, while the other attempts to distinguish between real and fake images. However, in this case, GPT serves as both the writer and editor, working to enhance its own output.
The Reflexion technique has proven to be effective in improving GPT-4’s performance in various tests, demonstrating its potential for significant advancement in AI development.


