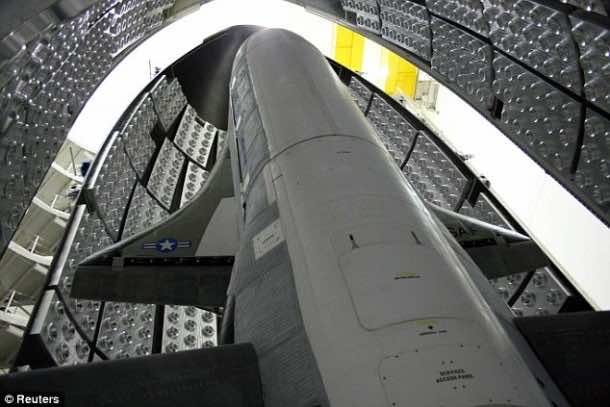
How many of you know about the X-37B space plane that is operated by Air Force? Exactly what do you know about it and its missions? Yes, there isn’t much detail. Why? Because it is basically a secretive experimental program that is being run by Air Force. The space plane is capable of staying in orbit for about 2 years and has blasted off again for the fourth time today. As of now, we still don’t know what’s on board. X-37B plane is also known as Test Orbital Plane.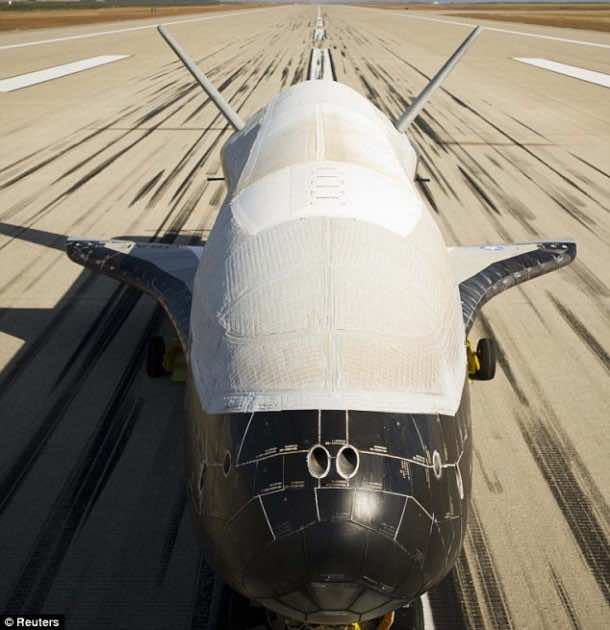
It shall be launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station like the previous three. It is a technology test bed that has been designed so that it orbits the Earth and then lands similar to like NASA’s old shuttles. The plane doesn’t require anyone to be on-board and is operated by robots. It is reusable and is about 29 feet long – that would be roughly one fourth the size of a NASA shuttle. So far, the longest X-37B flight lasted from almost 675 days with touchdown taking place last October.

NASA has a materials experiment on-board whereas the Planetary Society has arranged for a solar-soil demo. Air Force has only released information regarding a thruster experiment that will involve electric propulsion. Research team from Air Force has plans of checking out design modifications to ion thrusters which are already being used on some of the advanced military communication satellites. Altas V rocket was scheduled for 11:05 am today.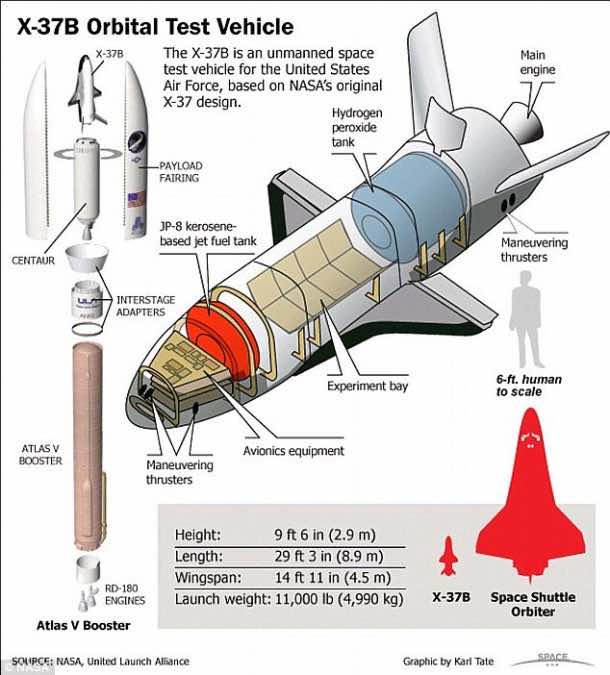
Despite all the secrecy, some information that did come through was earlier this month when the Department of Defense revealed some information about X-37B. Captain Chris Hoyler, Air Force spokesman said, “[We] are investigating an experimental propulsion system on the X-37B on Mission 4. The Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office will also host a number of advance materials onboard the X-37B for Nasa to study the durability of various materials in the space environment.”
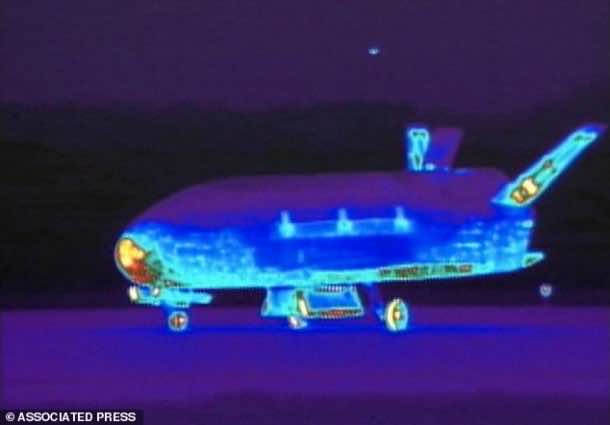

Steven Aftergood, secrecy expert at the Federation of American Scientists, said, “The US government has a bottomless appetite for sensitive information. As powerful as our intelligence satellites may be, they also have their limitations – most notably the limitations imposed by their orbital parameters. It’s conceivable that a spy plane would introduce new versatility into overhead reconnaissance.”



