The Mother of All Breaches (MOAB) has recently come to light as a colossal aggregation of credentials amassed from various data breaches over the years. Discovered by a team of researchers, this extensive database is a whopping 12 terabytes in size and contains tens of billions of credentials collected over decades.
Cybernews, the organization that unveiled MOAB, published a report revealing that the database comprises 26 billion entries and includes credentials from a wide range of companies. Chinese giants Tencent and Weibo, as well as prominent American social media platforms like Twitter, MySpace, and LinkedIn, are among the companies impacted.
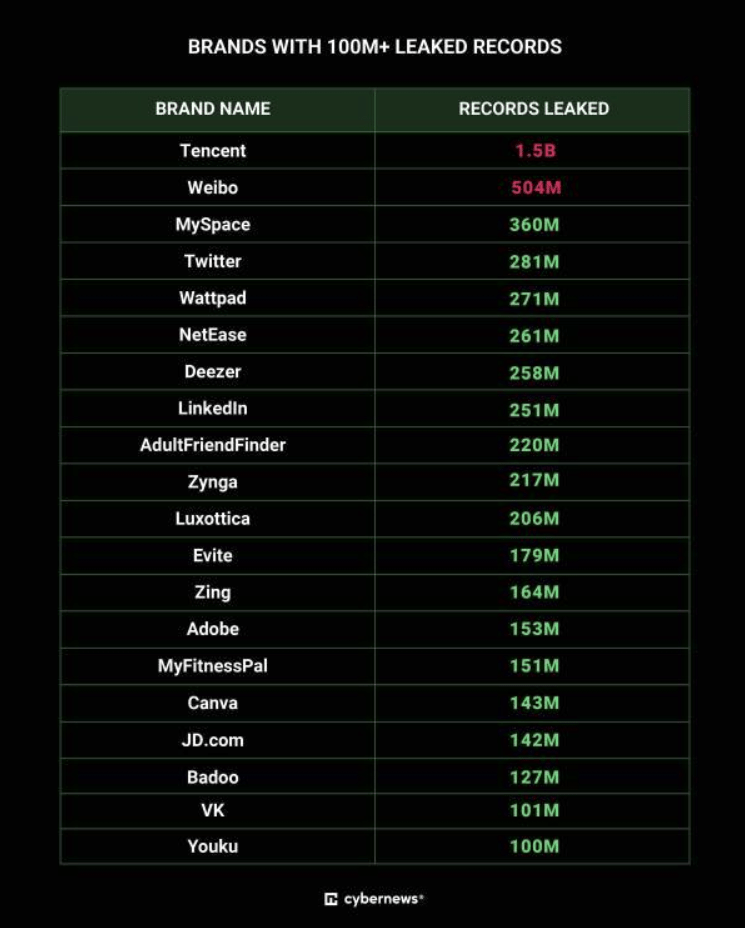
According to the researchers, the MOAB has been meticulously curated and is currently searchable, but only for affected URLs. However, the identity of the entity or individual behind the compilation remains unknown, and there is skepticism about it ever being revealed. The database is organized into 3,800 folders, each representing a separate data breach.
Despite efforts to curate and organize the information, researchers caution that duplicates are likely within individual folders. This possibility arises because users may find their credentials in multiple folders due to being exposed in past breaches.
Interestingly, the MOAB is not just a singular breach but rather a Compilation of Multiple Breaches (COMB). The sheer scale and depth of the database pose significant concerns for cybersecurity, emphasizing the need for users to remain vigilant about their online security practices.

While many of the credentials in MOAB are from older breaches, the risks persist as people often reuse passwords across various platforms. The report underscores the importance of using complex and unique passwords for each online account and advocates for the adoption of two-factor authentication whenever possible.
In conclusion, the discovery of MOAB serves as a stark reminder of the persistent challenges in securing personal information online and highlights the ongoing threats posed by large-scale data breaches. Users are urged to take proactive measures to safeguard their digital identities and employ best practices in password management and authentication.


