To carry out different types of operational activities on the surface of the moon, the Japanese firm GITAI has manufactured a robot through mutual cooperation with JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency). The mission aims to expand the integration of different technologies on the moon and to gain in-depth experience as well. This moon rover has been named R1 by GITAI, which also excels in developing a wide array of robots for different purposes.
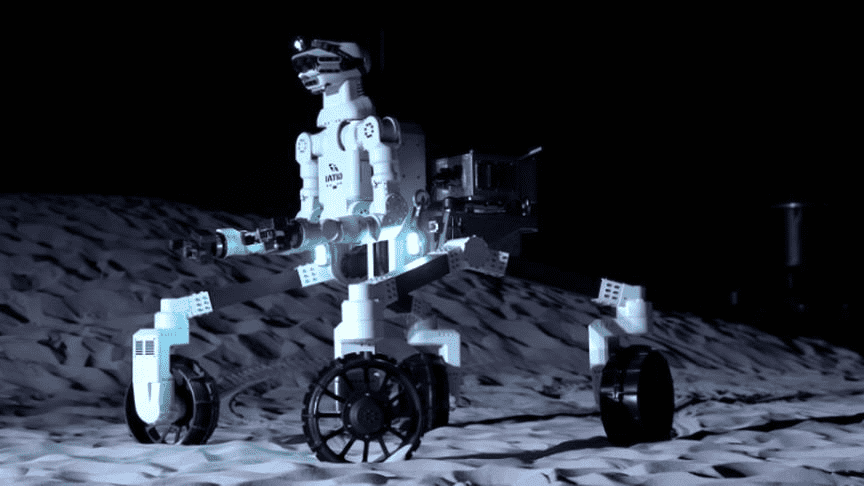
The automation is awe-inspiring, with the physical structure of the rover contemplating the look of a centaur—a creature having the legs and body of a horse, and the face and arms of a human. It has cameras attached to both of its eyes, has two claw-like arms, and consists of four legs like a horse. This is the most unique robot ever designed for the moon. We haven’t seen any moon rovers like this before.
To test the prototype, the scientists conducted an inspection by giving it a moon-like surface located at JAXA. It was more like a simulation of interstellar soil. It has been reported that the rover has efficiently swarmed and conquered this simulated lunar surface, which was comprised of several uneven terrains. The rover R1 was successful in navigating the uneven tracks and unpacking different wedges using its claw-like hands. Moreover, it also performed the task of fabricating the composition skeleton of the solar panels on the surface.
Coupled with this, the rover also underwent the pedagogy of collecting some samples of lunar rocks, which demonstrated its navigational capabilities. The design that emerged is exactly similar to that expected of the robots for the conduction of interstellar activities on the moon. NASA and International Space Station have also deployed their robots in space, especially the AI robot by the ISS, which was invented to “test human-machine interaction in space”, but neither of these robots possesses the humane characteristics of the R1.

With the ever-increasing urge to create permanent colonies on the moon by the developed countries like the US, Russia, and China, these types of robots serve the need of the hour to make the commercial missions possible in space in the future.


