In today’s automobiles, usually two types of steering types are prevalent:
1) Rack and pinion:
Rack-and-pinion steering one of the most prevalent steering system used on cars and small trucks.
Here’s how it works:
A rack-and-pinion gear set is usually covered by a metal tube, with the rack sticking out from the tube at each end. A tie rod or axial rod is used to connect each end of the rack.
Below is the diagram of the configuration of Rack and Pinion:
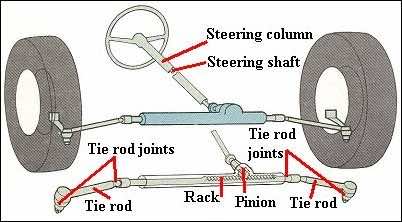
The pinion gear is attached to the steering shaft. When the steering wheel is turned, the gear spins, moving the rack. The tie rod at each end of the rack connects to the steering arm which is attached to the spindle.
This type of gearing mechanism as two main purposes:
1) It converts steering wheel’s circular motion into linear motion.
2) It causes a gear reduction, making it easier to turn the wheels.
Here’s a video of how a Rack and Pinion steering system works:
Variable ratio steering
This is actually a sub-type of the rack and pinion steering system.
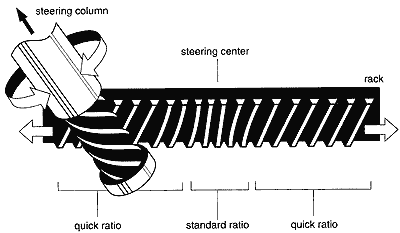
This rack-and-pinion is only different in the fact that it has a different tooth pitch (number of teeth per cm) in the center than at the ends. This makes the steering less sensitive when the pinion gear is close to the center position, but will make it move easier. When it is moving towards the far ends, the wheels begin to react more quickly to steering input, but the steering wheel will feel a bit heavier.
2) Recirculating ball / Steering box
Recirculating ball steering is the most commonly used steering system in heavy vehicles, trucks and the larger/heavier SUVs.
This system utilizes the parallelogram linkage, where the pitman and Idler arm remain parallel while the system absorbs shocks and additional vibrations.
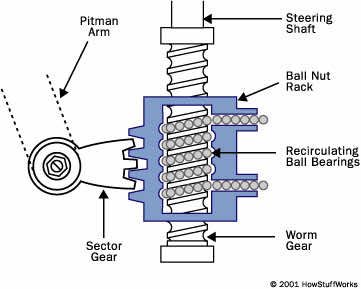
The recirculating-ball steering gear contains a worm gear. You can image the gear in two parts.
1) The first part is a block of metal with a threaded hole in it. This block has gear teeth cut into the outside of it, which engage a gear that moves the pitman arm.
2) The steering wheel connects to a threaded rod, similar to a bolt, that sticks into the hole in the block.
The Pitman arm is a steering component in an automobile or truck.The Pitman arm is a linkage attached to the steering box sector shaft, that converts the angular motion of the sector shaft into the linear motion needed to steer the wheels.
The steering wheel affixed to the steering shaft, and this shaft has threaded rod at the end, like a bolt. When the steering wheel rotates, it turns this rod with it. But instead of twisting further into the block, the rod remains fixed and in turn it moves the block. This block has gear teeth outside of it. These engage the sector gear which then moves the pitman arm.
One interesting thing about this gearing system is that the threads in the rod are filled with ball bearings. And these bearings recirculate through the gear as it turns – hence the name of the steering system.
The ball bearings serve two purposes:
– They reduce friction in the gear.
– If there were no balls used, the teeth would come out of contact with each other for a moment whenever the steering wheel would change its direction. This would cause the steering to feel loose.
Here’s a video explaining how this works:
Did you like this article? Would you like to add something more to the information?
Comment below!


