The creation of a novel supercapacitor material by researchers at the University of California, San Diego is pushing the limits of energy storage technology and might completely change the way that electric cars, boats, and electronics are powered. This novel material can function as a supercapacitor, storing energy for a variety of uses. It takes the form of a cloth composed of woven carbon fibers and conductive plastic.
This technology’s main benefit is that it can replace traditional batteries in a variety of applications, greatly lowering weight and prolonging the lifespan of electronic equipment in the process. Imagine electrical devices like AirPods lasting significantly longer between charges, or electric cars with greater range and faster charging periods.
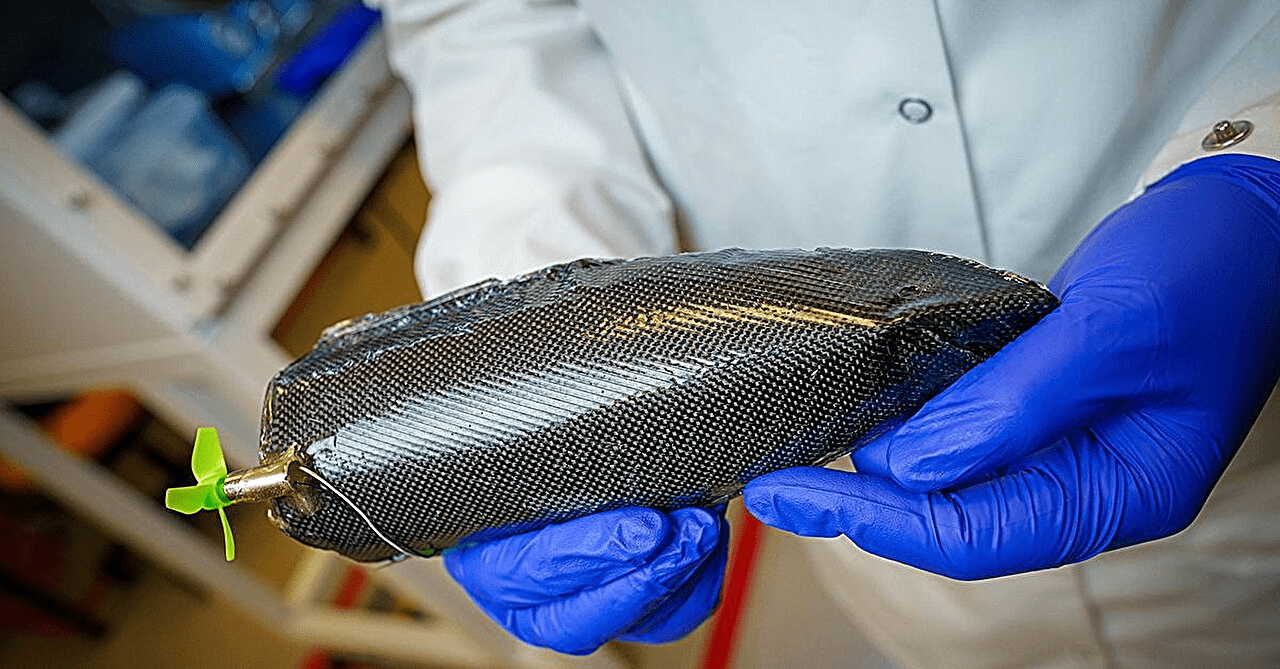

The researchers at UCSD demonstrated the capabilities of this material by building a miniature boat. This boat, constructed using the carbon fiber-based supercapacitor fabric, is a remarkable proof of concept. It is charged using a small solar panel on the top, and in a video clip released by UCSD, it can be seen navigating a small pool, showcasing the potential for this technology to power electric boats.
The boat is built using the same basic parts as a typical battery, including two electrodes and electrolytes to help with the charge and discharge cycles. Even while the technique seems promising, the researchers admit that there are still obstacles to be solved, especially with regard to production and energy storage.
In comparison to traditional batteries, the current supercapacitor design offers good power but falls short in energy storage. To make the supercapacitor material competitive with current battery technology, the team is therefore dedicated to increasing its energy density. Higher energy density and power density would be a revolutionary development in the field of energy storage, and that is their ultimate goal.
This research has the potential to drastically change how we power our electrical gadgets and vehicles. We could see lighter, more durable, and more effective energy storage alternatives if traditional batteries are no longer needed. This would eventually help the environment and enhance the functionality of electric cars, boats, and a variety of consumer goods. Even if more work needs to be done, the ground-breaking supercapacitor technology created at UCSD is a positive step toward an energy storage future that is more efficient and sustainable.


