GPT-4 astounded many users with its remarkable capabilities such as drafting lawsuits, passing standardized exams, and building a functional website from a hand-drawn sketch.
The more powerful GPT-4 has the potential to revolutionize the way we work, play, and create on the internet, surpassing its previous versions. However, its advanced features raise complex questions about the impact of AI tools on professions, student cheating, and our relationship with technology.
GPT-4 is an updated version of the company’s large language model, which uses vast amounts of online data to generate sophisticated responses to user prompts. Some early access users have shared their experiences and highlighted some of the most compelling use cases for the tool.
Analyzing pictures
To start with, OpenAI’s video demo showcased some of the most impressive use cases of GPT-4, including how a drawing could be transformed into a functional website in a matter of minutes.
In its announcement, OpenAI demonstrated how GPT-4 was able to explain a joke based on a series of images featuring a smartphone with the wrong charger. AI tools often struggle with picking up on the context required to understand the humor, making it a complex task.

The New York Times also tested GPT-4 by showing it a picture of the inside of a refrigerator and prompting it to generate a recipe based on the available ingredients.
Coding without a sweat
OpenAI claims that GPT-4 can write code in all major programming languages, making it a versatile tool for game development. According to Arun Chandrasekaran, an analyst at Gartner Research, GPT-4’s language capabilities could be used for various aspects of game development, including storyboarding, character creation, and content creation.
One user reported creating a simple drawing app in minutes, while another claimed to have coded an app that recommends five new movies every day along with trailers and details on where to watch them.
Clearing exams
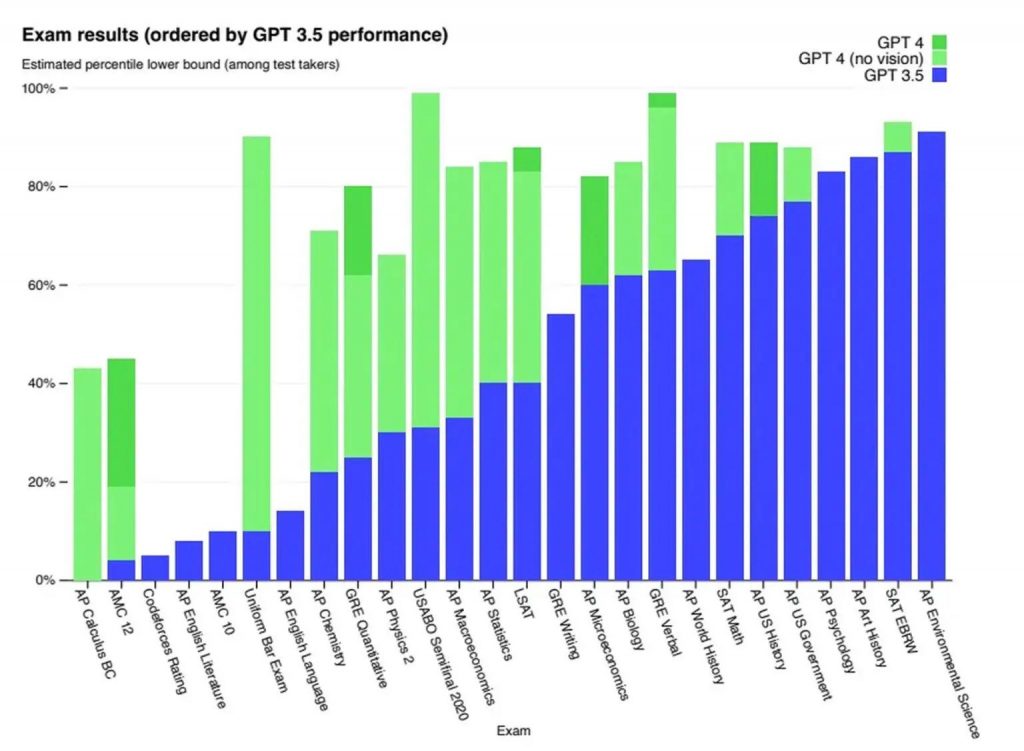
It has also demonstrated “human-level performance” on various professional and academic tests. For example, the latest version of the tool recently achieved a score that ranked in the top 10% of test takers on a simulated law school bar exam. In contrast, the previous version, GPT-3.5, ranked in the bottom 10%. Additionally, GPT-4 performed well on other tests, including the LSAT, GRE, SATs, and many AP exams, according to OpenAI.
More precise responses
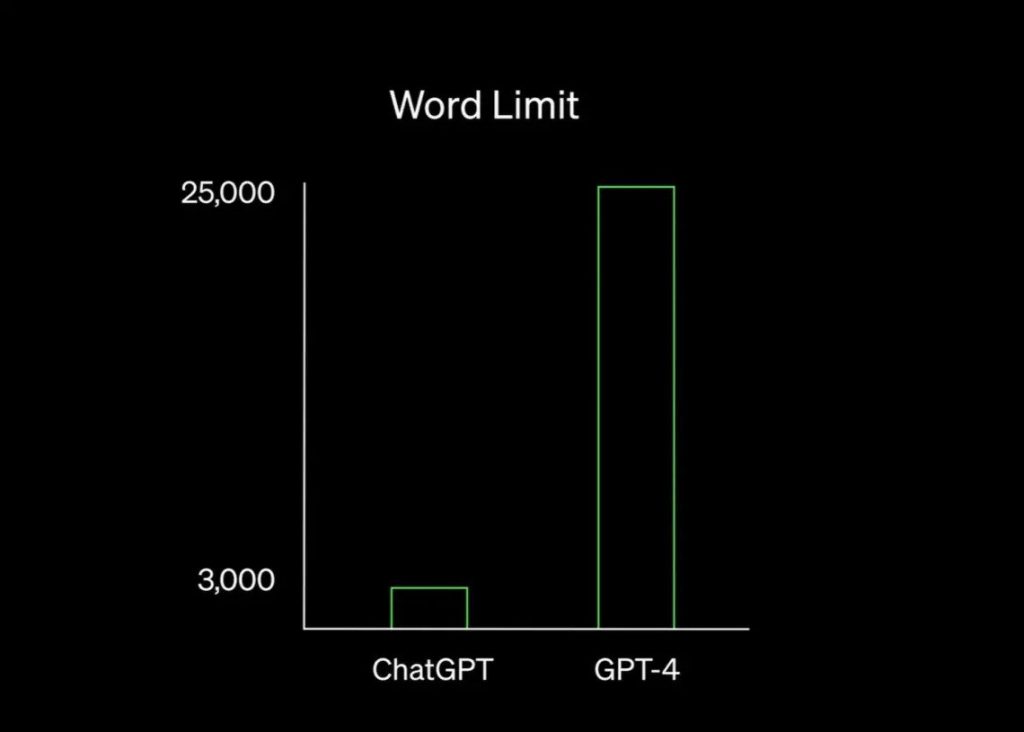
GPT-4 is now also able to produce longer, more detailed, and more reliable written responses, according to the company. The latest version can now give responses up to 25,000 words, up from about 4,000 previously, and can provide detailed instructions for even the most unique scenarios, ranging from how to clean a piranha’s fish tank to extracting the DNA of a strawberry.
OpenAI said the technology lacks knowledge of events that occurred before its data set cuts off and does not learn from its experience. It can also make “simple reasoning errors” or be “overly gullible in accepting obvious false statements from a user,” and not double-check work, the company said.
Gartner’s Chandrasekaran said this is also reflective of many AI models today. “Let us not forget that these AI models aren’t perfect,” Chandrasekaran said. “They can produce inaccurate information from time to time and can be black-box in nature.”


