The Sun is the closest star to Earth, but scientists are still trying to grasp the Sun’s core, which often generates tremendous solar winds that threaten our planet. While such research is underway, an international team of scientists has attempted to investigate a neutron star formed when a giant star dies in a supernova and its core collapses, resulting in neutrons.

The research claims to have measured the oscillations in a magnetar — a type of neutron star thought to have an extraordinarily powerful magnetic field during its turbulent moments as a first. However, the scientists discovered that the magnetar was released in less than a tenth of a second.
“Even in an inactive state, magnetars can be one hundred thousand times more luminous than our Sun, but in the case of the flash that we have studied — the GRB2001415 — the energy that was released is equivalent to that which our Sun radiates in one hundred thousand years,” lead researcher Alberto J. Castro-Tirado, from the IAA-CSIC, a Spanish government institute, said in a statement.

According to the study, the tenth-of-a-second explosion was discovered on April 15, 2020, amid COVID-19. The flare was “detected by the Atmosphere–Space Interactions Monitor instrument aboard the International Space Station.” Scientists have been analyzing the data since then.
Magnetars are neutron stars with the most strong magnetic fields known. They can hold half a million times the mass of the Earth. So far, just 30 of these objects have been discovered.
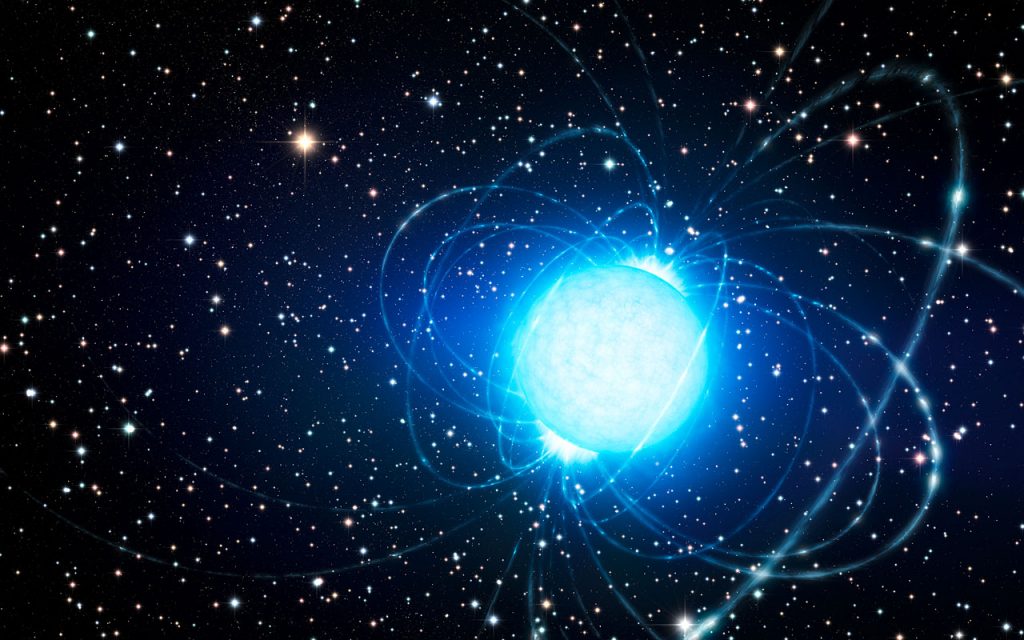
“These extremely high-frequency oscillations in the burst peak are a crucial component that will aid our understanding of magnetar giant flares,” the study added.
The findings were reported in the journal Nature.


