 The field that has benefited most from the advancement in science and technology is the medical science field. We are discovering new antidotes and safer methods to tackle ‘critical’ diseases. Speaking of critical diseases and complex surgeries, the surgery which is performed on heart is perhaps the most complex and time consuming. Conventionally, doctors made use of invasive stitches and staples to fix any holes in hearts. However, Harvard’s scientists have come u with a new superglue which is capable of holding heart tissues together.
The field that has benefited most from the advancement in science and technology is the medical science field. We are discovering new antidotes and safer methods to tackle ‘critical’ diseases. Speaking of critical diseases and complex surgeries, the surgery which is performed on heart is perhaps the most complex and time consuming. Conventionally, doctors made use of invasive stitches and staples to fix any holes in hearts. However, Harvard’s scientists have come u with a new superglue which is capable of holding heart tissues together.
One may very well ask, what’s the issue with conventional methods of ‘stitches and staples’? The answer is quite simple; a heap of problems. First of all, we need a watertight seal after the repair is done. Stitches and staples are not exactly a prime choice when it comes to wet environments and can’t take much pressure as well – beating of heart. Some materials which are used for the manufacturing of stitches and staples don’t fare well with blood and that can create some major problems. Superglue solves all of these issues! All you need to do is to expose it to UV light and voila; a watertight seal is here. Also, the superglue is immune to heart’s pressure, blood and the environment which surrounds heart.
 As always, the inspiration for this breakthrough came from nature; slugs and how their stickiness remains unaffected by water. This led the scientists to create a polymer which is flexible in nature and sets in seconds when exposed to UV light. Their test subjects were pig hearts that had holes in them. Application of superglue led to a miraculous recovery and the repair was successful.
As always, the inspiration for this breakthrough came from nature; slugs and how their stickiness remains unaffected by water. This led the scientists to create a polymer which is flexible in nature and sets in seconds when exposed to UV light. Their test subjects were pig hearts that had holes in them. Application of superglue led to a miraculous recovery and the repair was successful.
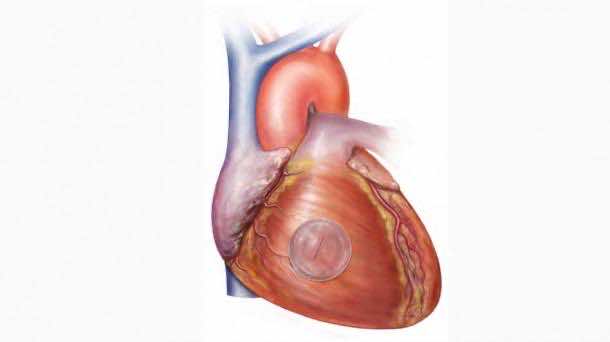 In case you’re wondering, Yes the superglue can be used for other internal organs and to do so, requires a very small tool kit. Hence, Super Glue will reduce invasive surgeries and the risks that come with it.
In case you’re wondering, Yes the superglue can be used for other internal organs and to do so, requires a very small tool kit. Hence, Super Glue will reduce invasive surgeries and the risks that come with it.


