Ian Brooke started the aerospace startup Astro Mechanica in 2021, and with its innovative turboelectric adaptable engine, it is revolutionizing flight. This innovative design offers a flexible option for both subsonic and supersonic flight by combining aspects of turbojets and turbofans. Astro Mechanica employs just eight people and uses state-of-the-art electric car motor technology to create engines.
The engine operates through a unique setup: a turbogenerator produces electricity to power electric motors that independently drive the compressor and turbofan. This configuration allows the engine to adjust air compression dynamically, optimizing performance for various flight conditions. On October 11, 2024, Astro Mechanica successfully conducted the first hot-fire test of its Gen3 engine at 30% power, marking a pivotal milestone.
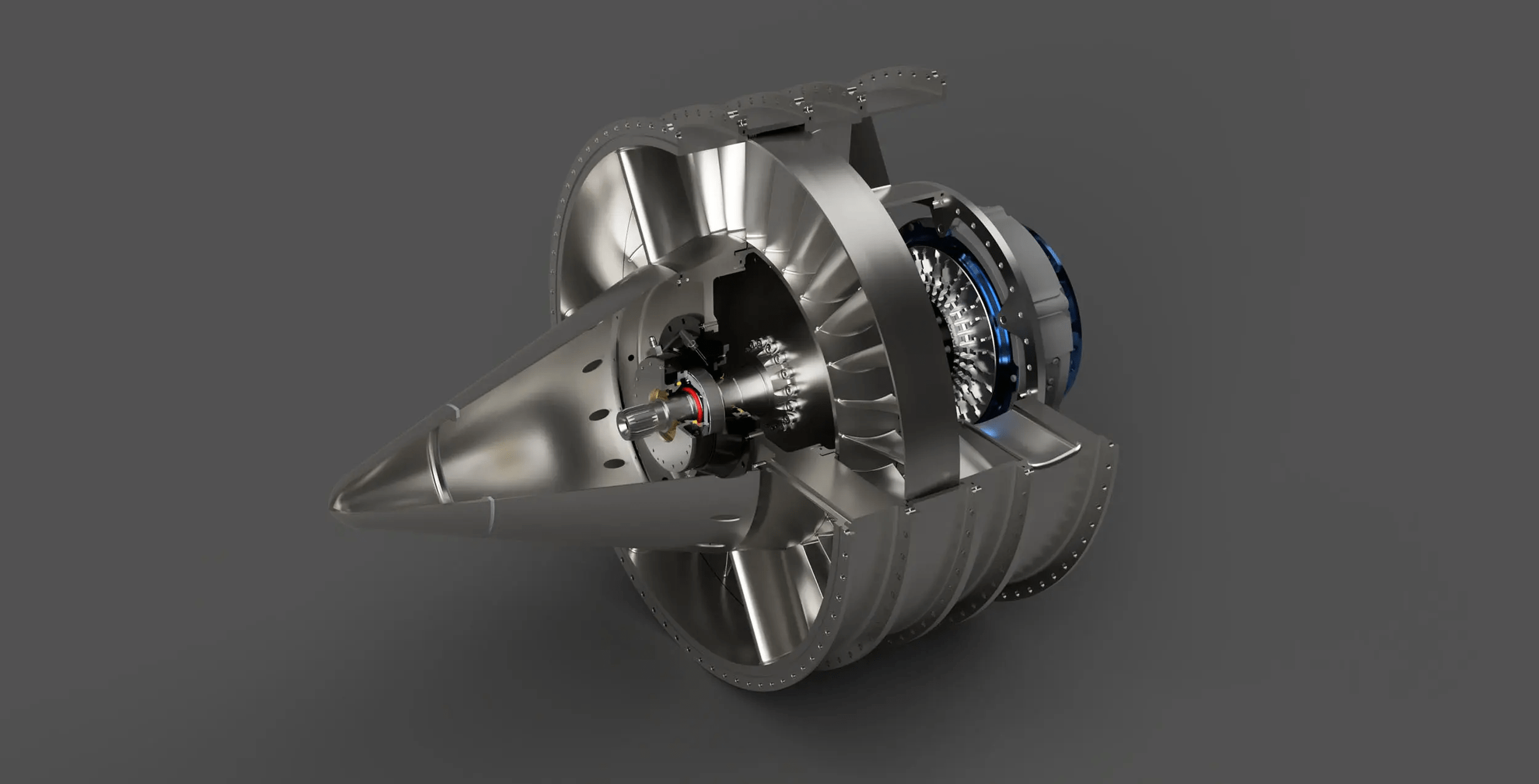
Traditional turbojets, while efficient at supersonic speeds, struggle with fuel inefficiency at lower speeds, as evidenced by the Concorde’s exorbitant fuel consumption—around 2 tons just to taxi. In contrast, turbofan engines excel at subsonic speeds but encounter drag and inefficiencies at high speeds. Astro Mechanica’s engine bridges this gap with three distinct modes:
- Mode 1: Electric motors spin a “blisk” (a bladed disk developed in-house) for efficient ground operations and subsonic flight without combustion.
- Mode 2: Turbojet combustion propels the aircraft supersonically, with electric motors powering the compressor to ensure optimal air intake.
- Mode 3: A fuel-only, ramjet-like configuration leverages Ram Pressure to achieve speeds potentially exceeding Mach 3.
Astro Mechanica estimates its engine could have extended the Concorde’s range by 61%, showcasing its potential to revolutionize aviation. This innovative design promises a future of fuel-efficient, versatile engines capable of transforming how we approach both commercial and military aviation.


