Well-known American computer chip manufacturer and technology company Nvidia has recently launched an incredible project – Earth-2- a digital replica of our planet. The development of such a simulation can serve as a basis for fundamental changes in the field of meteorology by allowing the development and analysis of global weather patterns in real time with an unimaginable level of detail. Additionally, this platform is available via an API and allows users to quickly create a range of AI-driven simulations, from global atmospheric situations down to local cloud cover; in extreme conditions, it can even cover catastrophic events like typhoons.
As the global economy suffers losses due to climate change-induced extreme weather, Earth-2 – the digital twin of Earth’s climate – assumes a pivotal role. Earth-2 is based on CorrDiff, an AI model by Nvidia, that allows for the generation of predictive images 1000 times faster than any of the currently available models, while also being 3000 times more energy-efficient. This efficiency breakthrough can help enhance early warning systems for natural disasters and significantly improve weather forecasting accuracy within seconds.
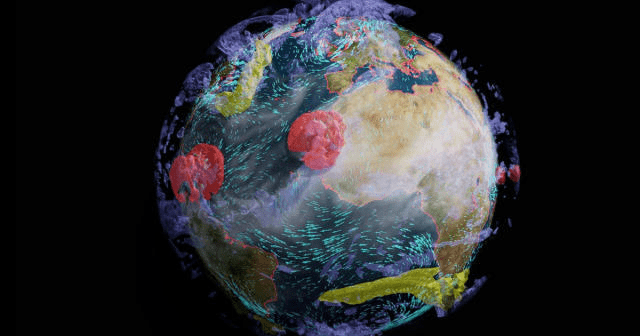
Earth-2 intends to help us prepare for and lessen the effect of climatic disasters, which are becoming more common, according to Nvidia CEO Jensen Huang, who also emphasized the project’s urgency. Governmental organizations, like the Central Weather Administration in Taiwan, are already preparing to use Earth-2 to improve their modeling of extreme weather events and predict the exact sites of typhoon landfalls.
Thanks to the emergence of generative AI tools, the demand for Nvidia’s GPUs in the tech industry has surged. Earth-2 is just one more example of Nvidia’s technological prowess and dedication to solving important global issues. By concentrating its AI know-how on extreme weather and climate change, Nvidia is positioned to significantly influence how we respond to these pressing problems. The effectiveness and long-term accuracy of Earth-2, however, are still up for debate, raising concerns about its potential future impact.


