Researchers have discovered a Giant Arc of Galaxies that owes to overturn our understanding of Cosmology. It is a breakthrough reveal because it defies the human narrative, saying, “matter in space is distributed equally.” The earlier concepts that scientists have entailed on cosmological principle says that galaxy clusters are distributed in an equal pattern. However, the newfound Giant Arc could upend our current understanding.
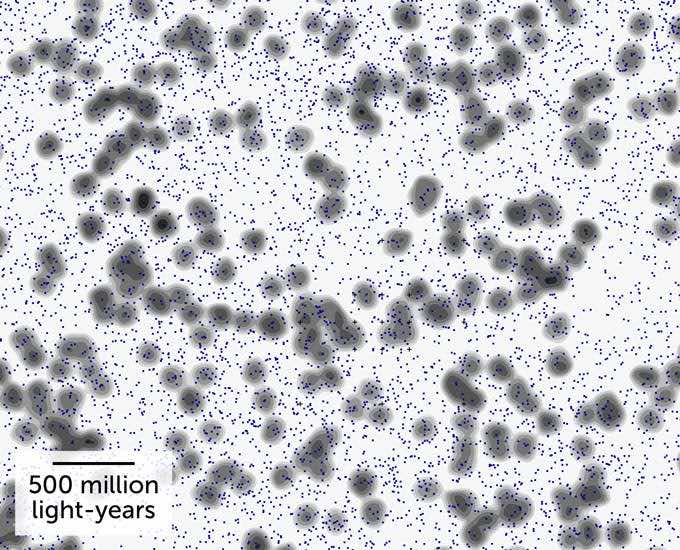
Researchers found that the Giant Arc of Galaxies stretches for about 3 billion light-years, roughly making up the 15th of the observable universe. They also revealed that the Giant Arc consists of several galaxies, galactic clusters, and infinite gas and dust.
While attending a virtual conference, a cosmologist from the team who made the discovery, Alexia Lopez, said, “It would overturn cosmology as we know it. Our standard model, not to put it too heavily, kind of falls through.” It is a very big deal, she added.

Lopez and her colleagues referred to the arc of galaxies as the ‘Giant Arc,” given that it is a 1/15th portion of the total observable space. It defies the previous cosmological principle explained by scientists. Astrobites, the renowned astrophysical literature journal, notes that cosmological principle is not a physical law. Instead, it is a guiding heuristic that seconds on the point that matter is equally distributed in space. However, the Giant Arc found by the University of Lancashire Cosmologists says otherwise and presses that there is an unequal distribution of matter in space.
The researchers were able to make the reveal after observing light from 40,000 quasars, the luminous cores of galaxies, which are also home to the supermassive black holes. Scientists and researchers find out about space and our universe by observing light signatures coming from these quasars. The detectable light pattern reaches earth after being absorbed by atoms and objects around the galaxies, allowing the scientists to dive into the insights of space, aided by these unique light signatures.
The team of Cosmologists from the university of Lancashire detected the incoming light from these quasars forming a giant arc, stretching across one-fifteenth the radius of the observable universe. They revealed an image of their findings in which you can see the giant arc formed, appearing to be a smile-shaped curve in the center of the picture.