From designing blood vessels and drug capsules in lab (synthetic biology) to tapping nanoparticles and nanotubes (nanobiotechnology) for cancer research, these novel emerging technologies might revolutionize medicine in near future.
1. Surgical Robots:
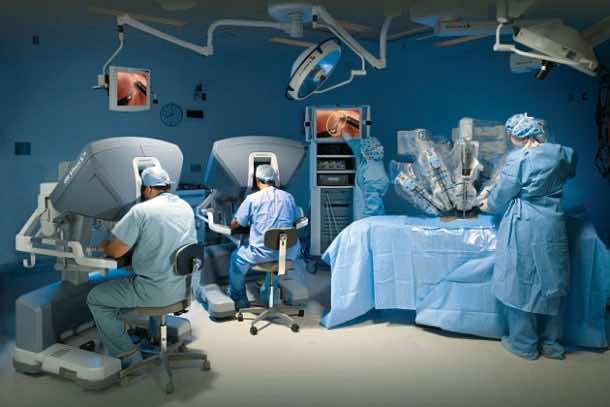
Surgical robots have aided in carrying out remote surgery, minimally invasive surgery and even to the extent of unmanned surgery. Owing to the robotic machinery, surgery is carried out with enhanced precision and miniaturization. The incisions are smaller resulting in decreased blood loss, less pain, and rapid recovery.
At Vanderbilt University, surgical robot that used an ultraminiature mechanical wrist instrument to make incisions so small they need only a Band-Aid. The robot consists of an arm made of tiny concentric tubes that become smaller as they extend out, thinning to a radio antenna, with a mechanical wrist at the end. The wrist is less than 1/16th of an inch thick and can bend up to 90 degrees.
In the past decade, surgical robots have significantly expanded the use of laparoscopic surgery, which requires incisions of just 5 to 10 millimeters. It is hoped that this technology will advance needlescopic surgery, in which the incisions are less than 3 millimeters.
2. Cancer Screening:

The most important strategy of counteracting cancer is its early detection, but cancer does go unnoticed until it’s too late. Vadim Backman, a biomedical engineer and professor at Northwestern University, is working to improve early cancer detection using a noninvasive diagnostic test. His lab designed an instrument that combines traditional microscopy with spectroscopy- a microscope that uses light to measure the tiny aberrations and abnormalities in cells.
Lung tumors can be difficult to spot early on without expensive imaging scans, which often aren’t recommended for low-risk patients. Backman’s test can detect changes in the structure of cell samples, taken from patients’ cheeks, that indicate lung cancer may be developing as the tumor appearing in a particular location also affect the nearby cells.
Cancer screening aims to detect cancer before symptoms appear. This may involve blood tests, urine tests, other tests, or medical imaging. The benefits of screening in terms of cancer prevention, early detection and subsequent treatment must be weighed against any harms.
3. Bio-engineered Blood Vessels:
Humacyte Inc., a startup, is notching big advances in biomedical engineering as they have a designed a blood vessel for patients undergoing kidney dialysis. The company uses donor cells to grow the human tissue needed to make the blood vessels. It cleanses the donor cells from the vessels before implanting them, to prevent rejection by the recipient’s immune system.
Two midstage studies showed patients’ natural cells merged with the engineered blood vessels, which could make them less prone to infection and more durable than the metal tubes often used to facilitate blood flow in dialysis patients. The next stage would be tissue engineering and organ engineering but this vision does not seem very far-fetched now.
4. Neuromodulation:
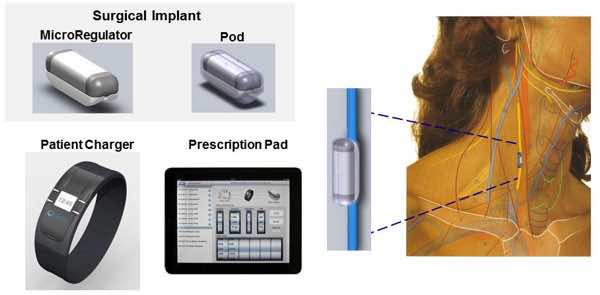
SetPoint Medical is working on a device that uses electrical stimulation to treat inflammatory diseases such as Rheumatoid Arthritis (inflammation at joints) and Crohn’s disease (inflammation of intestines).
Studies have shown that high activity of Vagus Nerve in the body can help reduce the inflammation. By implanting a small electrical stimulator near the vagus nerve in the neck, SetPoint’s device is designed to jump-start the nerve’s activity. The first human studies of SetPoint’s device are set to begin in the next six to nine months, announced by the company. The device is years away from potential market entry, but it could reduce the need for drugs with side effects.
5. Smartstop: smoking-cessation device:

Cigarette smoking is one of the major causes of Lung Cancer and deaths around the world but the most commonly used methods for quitting have not proven very effective whether we talk about nicotine gum or patches.
Chrono Therapeutics, is betting it can combine smartphone technology with a gadget similar to the patch to improve quitting rates. Smokers wear a small electronic device that is timed to deliver nicotine at higher doses when cravings are strongest, such as in the morning after waking up and after meals. Since nicotine can interfere with sleep, the device shuts off when the person goes to bed.
The device connects with a smartphone app that uses gamification techniques to help users track their progress and deliver tips on how to deal with cravings. Chrono hopes to have the product on the market in 2018 after human trials.


